Overview on project results
Results Human
interaction behavior
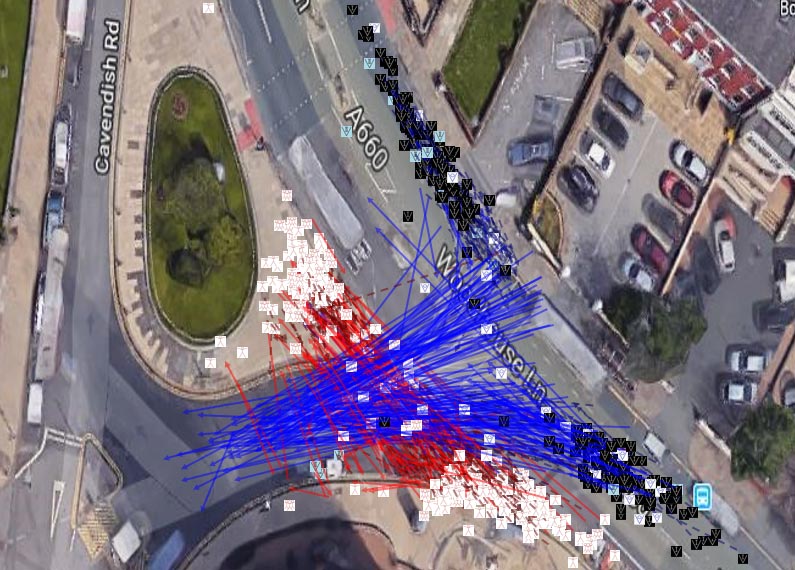

- Definition of interaction terminology
- Several observation studies on human-human interaction in Greece, Germany and the UK
- Traffic participants tend to avoid conflicts; Interactions are more likely to occur when the vehicle is driving slowly; Pedestrians mostly focus on implicit vehicle cues rather than explicit communication
Results
Intention recognition
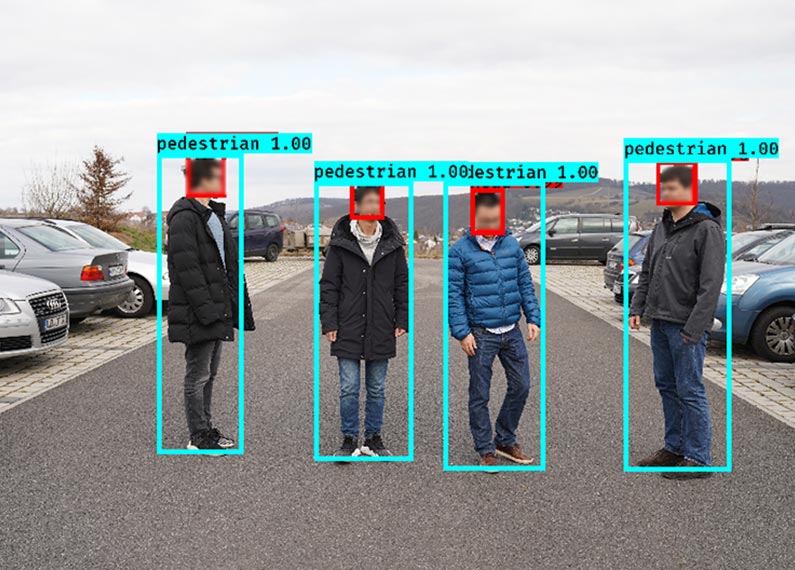
- Risk analysis framework for the prediction of traffic participants location
- Pedestrian intention prediction using the semantic map and behaviour models of other traffic participants
- Novel deep learning techniques, for classification of pedestrians’ head orientation and hand waving gestures
- Hidden Markov model for vehicle maneuvers recognition and generation of intention-aware trajectory.
- Extended vehicle prediction trajectory via fusion of intention-based with typical motion-based
Results Communication and
Cooperation Planning Unit
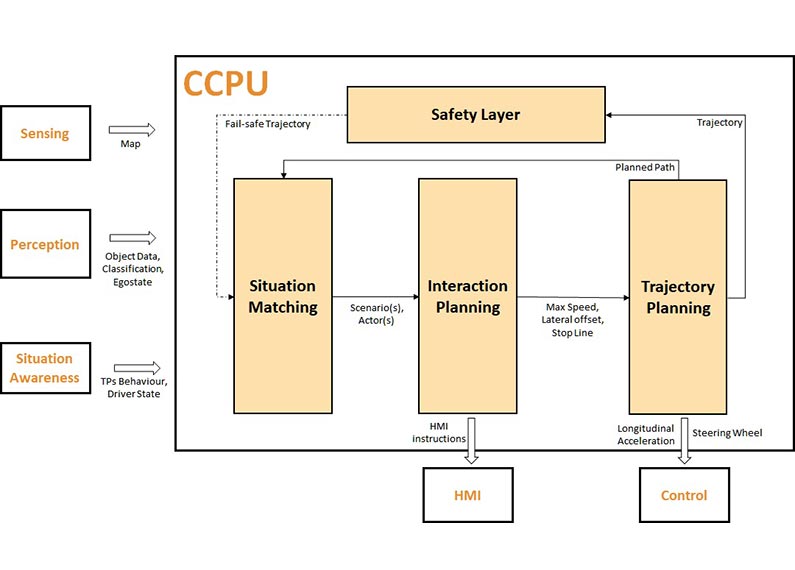
- Recognition of traffic conflicts between Automated Vehicles and other traffic participants
- Implementation of reaction strategies according to the identified situation (future path constraints, candidate actors for HMI/eHMI interaction)
- Integration of internal and external HMI to enable human-like interaction
- Development of safety layer for emergency situations
Results
HMI/eHMI
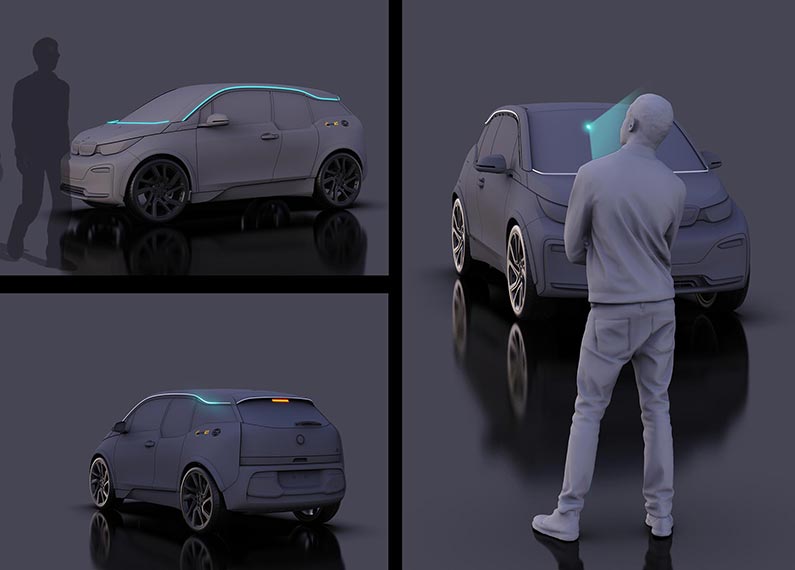

- Two interaction strategies defined: intention-based & perception-based strategy for HMI/eHMI
- Two eHMI technologies developed and implemented: 360° Light Band & Directed Signal Lamp
- Two iHMI technologies: Light Band & Automation Display
Results
Evaluation methodologies
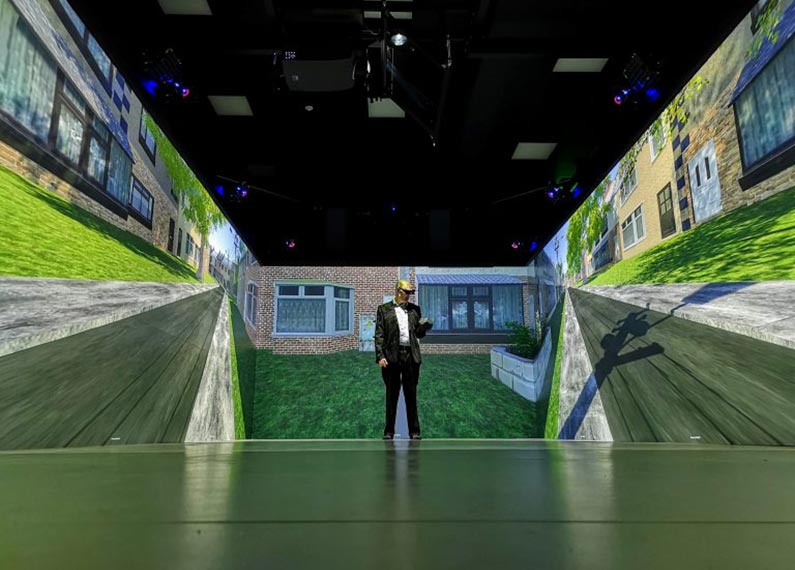

- Evaluation criteria and methodologies derived for Automated vehicles
- interACT demonstrators evaluated in test-track studies, while eHMI/iHMI solutions were also evaluated using driving and pedestrian simulator
- Impact assessment carried out to understand the effects of the interACT solutions on safety, traffic flow, criticality, comfort, and acceptance

